Role of Additives in Optimization of Flyash in Cement
S.K Agarwal and Preeti Sharma, Central Building Research Institute, Roorkee
This paper deals with the effect of various additives in optimizing the flyash content in portland cement. The study showed that with the use of various additives like naphthalene–based superplasticizer, calcium nitrite, calcium formate or blend of these additives. It is possible to load up to 35% of flyash in ordinary Portland cement compared to around 25% of flyash present in Indian portland pozzolana cement. The 35% limit is the upper limit fixed by Indian standard. The 28-day compressive strength of cement with 35% flyash incorporating various additives is comparable to control PPC. Effect of flyash replacement by sand has also been studied.
Introduction
India at present produces about 120 million tons of cement, out of which 30-40 million tons of cement is blended. The major blended cements are predominantly Portland pozzolana PPC (flyash), and Portland slag (PSC). About 30% of flyash is being utilized by various agencies. Thus, there is tremendous pressure for its utilization from environmental angle. The portland pozzolana cement is being sold in the market as 53MPa, composite cement etc. This PPC contains 20-25% flyash. The cement manufacturers are envisaging that by 2010 the share of the blended cements will be about 60% with major share of PPC. It is only possible if more fly ash is loaded in OPC. Keeping this in view, there is scope of loading more flyash in OPC. In India, up to 35% flyash is permitted under BIS 1491-1991.Many research workers have used additives either as grinding aids for clinker or improving the properties of cement. Effect of additives on individual components of cements have been studied (1-6) extensively to know the hydration behavior.
This paper presents the results of an investigation on the effect of additives in optimizing flyash content in OPC. The compressive strength of cement mortars incorporating two grades (I&II, BIS 3812-2003) of flyash has been chosen for the present study.
Experimental
Materials
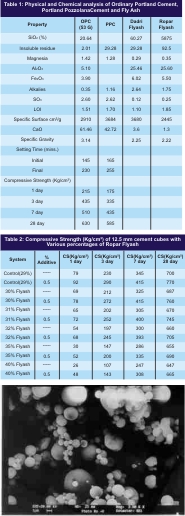
53 grade OPC conforming to BIS 12269 and PPC (29% flyash) was used in present study. The physical and chemical properties of OPC and PPC cements are given in Table 1.Two flyashes one from Dadri and other from Ropar were taken for the present study. The physical and chemical properties of flyash (Dadri and Ropar) are also given in Table 1.
Powdered naphthalene sulfonated formaldehyde condensate, calcium nitrite and calcium formate were procured from the local market.
Method
Stock of Ordinary Portland cement with various percentage of flyash was blended thoroughly using powder mixer.Casting of 12.5mm cement cubes (OPC) with various percentages of flyash (Ropar and Dadri) were cast with and without additive (SNF) at water content required for the consistency of control cement. The cubes were demolded after 24 hrs. and kept in water at 27 ± 2oC. The compressive strength at 1, 3, 7 and 28 days is given in Table2-3.
The effect on compressive strength by replacing flyash with sand has also been studied and results are given in Table 4.
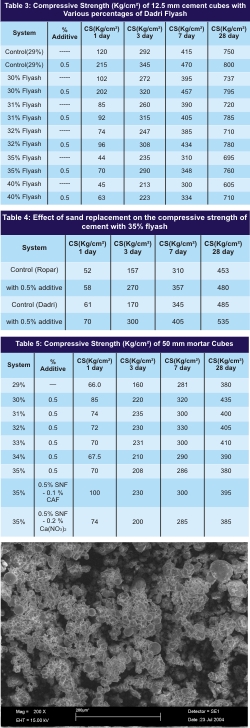
The casting of 50mm cubes of mortar (1:3) with and without additives (SNF, calcium formate and calcium Nitrate) were cast and cured at 27±2ºC. The compressive strength at 1, 3, 7 and 28 days were obtained. The results are given in Table 5.
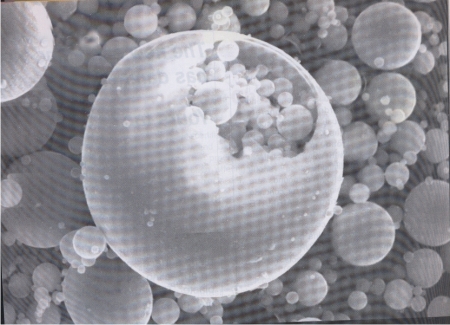
Scanning electron micrograph of Dadri and Ropar flyash was determined and shown in figure 1 and 2.
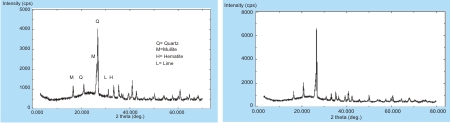
The X ray of both the flyashes was also taken and shown in figure 3 and 4.
The pozzolanic reactivity index of Dadri flyash is 120 and Ropar flyash is 90. The dose of SNF was optimized and found 0.5% by weight of cement in the present study.
Results and Discussion
Effect of additive (SNF) on compressive strength of cement incorporating Ropar flyash:
Table 2 presents the compressive strength data of various percentages of flyash cement with and without additive. The control cement contains 29% flyash, which was supplied by the manufacturer. It is clear from the table that with addition of 0.5% additive (sulfonated formaldehyde condensate powder), up to 35% flyash blended cement, the compressive strength at various ages of 1, 3, 7 and 28 days are comparable to the control cement. However, when fly ash content is increased to 40%, the 3 and 7 day compressive strength is about 25-30% lowers than the control, however at 28 days, it is only 5% lower when compared to control.
Effect of SNF on Compressive Strength of Cement Incorporating Dadri Flyash:
Effect of Sand Replacement
In order to find out the contribution of flyash in the strength development of cement, flyash was replaced by sand in the 35% mix. In case of Ropar flyash at 28 days, the compressive strength of cement without additive, there is drop of 54% and 49% with additive. In case of Dadri flyash also the drop in compressive strength is similar. It can be concluded from the observation that the contribution of flyash in strength development is 54 and 49%.Effect of SNF on Mortar
Table 5 represents the data of 1:3 mortars. The compressive strength of control system with 29% flyash has been compared with mortar with 35% flyash cement and with 0.5% additive. It is clear from the table that compressive strength at 1, 3, 7 and at 28 days it is about 5% more up to 33% flyash cement and it is at par with control up to 35%. When calcium formate and calcium nitrite is added along with SNF the 1-day strength has been found to be 50 and 30% more than control. However, at 28 days, it is similar to control system.The addition of superplasticizer in cement disperses the cement particles and allows the glassy content of the fly ash to react effectively with the lime liberated by the hydration of the cement to form CSH.
The increase in flyash content from 29% to 35% in a cement plant of 5000 tons capacity per day, extra 462 tons flyash can be loaded. It has been estimated that including the cost of superplasticizer (0.5%), it is possible to save around $2100 per day. It is not only the saving in terms of cost but from environmental point of view.
Conclusion
- It is clear from the present studies that with the addition of powdered SNF. It is possible to increase the flyash content up to 35% in OPC.
- The addition of flyash has no negative effect on the compressive strength of cement up to 35%.
- The study will help to utilize more flyash in OPC, thereby helping to save limestone used in the manufacture of clinker and hence environmental pollution caused due to CO2in the clinker production.
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to Director, Central Building Research Institute, Roorkee for pursuing the work in the lab. The paper is being published with the permission of Director, CBRI, Roorkee.
NBM&CW March 2009


















