SoilTech: Road Engineering, Design & Construction

The good Minister can only encourage so much. It is time for road engineers to do their part and to stand up and to courageously transform the road construction industry through innovative design and engineering.
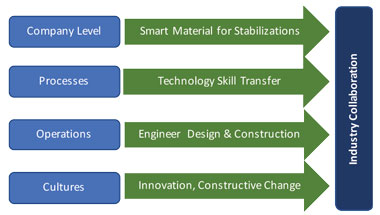
The road construction and engineering industry strongly affects society, the economy and the environment as a whole. It touches the daily lives of everyone as quality of life is heavily influenced by road infrastructure and accessibility to markets.
Compared to many other industries, the construction industry has traditionally been slow at technological development. It has undergone no major disruptive changes in design. Many road designs are still based on the Scotsman John Louden Macadam, who pioneered roads in the 1820s.
Considering that most quarries are owned by the cement conglomerates, it is no small wonder that there has been little advancement in road construction technologies. It is in the absolute interest of these corporates for road design and construction to remain the way it is. At the IRC conference in Bangalore, 2014, Professor Kadiyali categorically stated, that India consumes enough aggregate annually, to build a road around the world every year, 6 m wide by 600mm deep. Obviously, this trend is unsustainable and needs to be changed as a matter of urgency. From a road construction perspective, it is the duty of engineers to find alternatives for re-designing roads and reducing aggregate consumption.

Given the sheer size of the road construction industry, even a small improvement would provide substantial benefits for society. The Indian road construction industry is ripe for progressive change, with the Minister of Roads advocating the need to consider alternative stabilizers.
Unfortunately, too many road engineers are like sheep and still prefer to copy-and-paste from road manuals, instead of doing what they were trained, i.e. road engineering.
It is companies and individuals themselves that should spearhead the industry transformation. Tremendous opportunities are available through the application of new technologies, materials and tools. Embracing these new technologies could mean the difference between progressive growth or stagnation in companies involved with road design and construction.

Smart Materials
SoilTech Mk. III - a third generation polymer stabilizer is supplied throughout India, to the roads sector by Kaveri Ultra Polymers. SoilTech Mk. III has been used in the mining industry for more than 15 years on heavy haul roads, throughout Southern Africa. Two-axle mine haul trucks weighing in excess of 300 tons use these all-weather roads 24 hours per day throughout the year. The load on the rear axle of a 300-ton haul truck is 210 tons. That is 30 times the international ESAL maximum(80kN) for a single axle. Now imagine applying this technology on a standard municipal or provincial road where the single axle specifications may not exceed eight tons of loading. SoilTech Mk. III polymer stabilizer enables and empowers companies to;
- Reduce the consumption of aggregate
- Reduce construction time
- Reduce costs and improve profits
- Complete more projects in a calendar year
- Reduce carbon footprint per kilometer by 97%.
- Customer’s road being constructed in reduced time and at lower costs.
- Longevity and performance of the road being extended with less maintenance required.
- Consulting Engineers gaining prestige with customers for forward thinking and increased project completion time.
- Construction companies being able to optimise equipment with reduced construction time, resulting in improved financial return.
- A positive environmental impact with less aggregate consumed, reduced diesel consumption, and reduced CO2 emissions.
“Smart Materials are available to everyone throughout India. We are not a construction company and we do not compete with the road industry players. Instead, we assist the industry by supplying products, doing skill transfers and assisting partners with innovative road designs, via a team of PhD engineers, Dr. Alex Visser & Dr. John Mukabi” – Nicholas J. Muller, CEO Polymer Pavements, South Africa
NBM&CW June 2018



















