STP’s Epoxy Flooring

STP's Specialty Chemicals and Additives Division manufactures a staggering array of products including Admixtures, Grouts, Waterproofing treatments, Epoxy flooring, floor hardeners, Tile Adhesives, Sealants and repair compound. The company has earned wide acclaim for its high performance Epoxy Flooring and Chemical Waterproofing products. It has now developed a wide range of Epoxy Floorings.
What is Epoxy?

General Definition
Epoxy flooring is chemically cured mass of Polymer (Bisphenol - epoxy resin with Polyamine / Polyamides / Cycl - aliphatic amines etc.). It is formulated by various Polymers, hardeners and graded filler.Why Epoxy Flooring?
- Chemical Resistant
- Abrasion Resistant
- Aesthetically good
- Discourage growth of bacteria / fungus
- Impermeable for variety of oils / grease
- Better compression strength to that of PCC
- Does not allow dust to adhere
- Easy to maintain
Features of Epoxy Flooring
- Tough
- Joint - less
- Monolithic
- Hygienic
- Chemical Resistant
Types of Epoxy Flooring
- Self - leveling Epoxy Flooring Topping
- Epoxy Screed
- Coatings - High Build and Low Build
- Antistatic Floorings
Self - leveling Epoxy Flooring Topping
Shali Deck SL - Three component system consisting of Comp A – Base Comp B – Hardener and Comp C – Filler. Self – leveling Shali Screed SL can be applied from thickness of 500 micron to 2000 micron. Suitable for floors where there is light / medium trolley movement, hospitals, kitchens, pharmaceuticals, automobile plants and workshops.Epoxy Screed
Shali Screed – Three component system consisting of Comp A – Base Comp B – Hardener and Comp C – Filler. It can be applied from thickness 3 mm to 5 mm. It is Ideal for floor where there is heavy trolley movement.Shali Screed 2000 – it's a new product. Applied at a thickness of 2 mm.
Self - leveling Screed

Shali Screed SL UL Three component system consisting of Comp A – Base Comp B – Hardener and Comp C – Filler Applied at a thickness of 1.5 mm to 4 mm. It is applied as an under - layment. This saves cost.
Epoxy Coatings
Epoxy coatings can be applied at thickness of 90 micron to 200 micron.ShaliPoxy LB – Two Component System consisting of comp A- Base and comp B Hardener. It can be applied on the wall.
ShaliPoxy FC – Two Component System consisting of comp A - Base and comp B Hardener. It can be applied on the floor as well as walls.
ShaliOl PU (Polyurethane Aliphatic based) – Two Component System consisting of comp A – Base and comp B Hardener. It is UV resistant and can be applied on the walls as well as on the floor.
Antistatic Flooring
Antistatic flooring is done in the areas wherever static current is generated and requires decapitating the charges, in order to protect the electronic components like Integrated Circuit etc. Mainly applies for electronic manufacturing firms, Operation theaters, Companies which has installed sensitive equipment etc.Basic Requirement Before Installation of Epoxy System
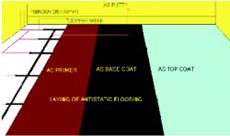
Schematic diagram for laying Antistatic Flooring
- Concrete should be minimum 28 days old.
- Concrete should be finished properly.
- Moisture content of the floor should be below 5%.
Guidelines when visiting the site
- Identify the type of substrate to be coated e.g., concrete, kota stone etc.
- Check the moisture content
- Check for any water leakages from roof / wall
- Any chemical / solvent spillages and its concentration
- Type of traffic movement and load
- Check for any cracks or pot holes on the substrate
Common method of preparing surface
- Grinding
- Sandering
- Scarifying
- Chemical cleaning (acid etching)
- Burning if oil / grease on the floor
- Cleaning to remove dust / debris etc.
Application

- Basic surface preparation and precautions before application to be followed as per general Epoxy Floorings.
- After proper surface preparation, cut the groove of the size 5mm x 10 mm along the periphery (20 cms away from the walls) and then divide the floor area of room in such a way that equidistant is maintained between grooves and ensure that the distance between 2 grooves does not exceed more than 1 mtr and should not be less than 75 cms.
- After cutting the groove, insert the copper wire into the groove. Ensure that continuity is maintained without breaking the connection. Extend any one end of the wire in a room for earthing (as desired by customer).
- Fill the groove with Antistatic Putty.
- After putty dries, grind excess of putty for levelling to the substrate
- After grinding of putty clean the whole area to ensure the whole area is free from dust.
- Apply the Antistatic Primer as per coverage. Allow the primer to dry.
- After primer dries, apply the Base coat as per coverage. Application method to be followed as that of ShaliDeck SL. Allow base coat to dry.
- After base coat dries, apply ShaliScreed SL AS Top Coat as per coverage. Application method to be followed as that of ShaliDeck SL.
- Allow the Top Coat to dry and foot traffic should be allowed only after 24 hrs of curing.
Electrical Properties
Surface Resistivity As per ASTM D 257 at lab. Temp.23 + 2oC RH : 50 + 5%1 X 104 - 1 X 106M ohms STATIC DECAY TEST (Time to decay to 10% of peak charge) 0.03 sec.
Coverage of Antistatic Flooring
- Antistatic flooring can be applied at a thickness of 3mm to 5mm.
- 1.5 Kg AS Primer will be sufficient for 6 m2 for 150 micron thickness.
- 5 Kg AS Base will be sufficient for 3.85 m2 for 850 micron thickness.
- 10 Kg AS Top Coat will be sufficient for 3.3 m2 for 2 mm thickness.
NBM&CW March 2009



















