Construction Sector: Current Scenario and Emerging Trends

After recording a spectacular growth of over 12%, more than the country’s GDP in the past half decade, the Indian construction sector all of a sudden lost stream in last fiscal largely due to global financial turmoil. Not just this, the turmoil tremors created multiplier impact across sectors including steel, cement, power, petroleum, aluminum, IT and ports, besides badly Bruising the Indian economy.
But few sectors such as telecom, urban infrastructure, railways, oil and gas, which are also generating large share of construction activities have not been affected badly. These segments have registered a noticeable growth in project orders from centre, states, and local firms. However, orders from overseas firms have drastically dwindled.
Current Global Scenario

Speeding Infra Spending
The government has initiated innumerable initiatives to lift the sector from its current dormant conditions. The measures include authorizing the Indian Infrastructure Finance Company Limited (IIFCL) to raise Rs.100 billion by issuing of tax free bonds to make highways and port projects funding worth Rs. 250 billion available to the sector. In order to finance projects worth Rs. 750 billion over the next 18 months, the IIFCL has been given permission to raise additional funds worth Rs. 300 billion.Other measures include liberalization of the external commercial borrowing (ECBs) policy, revision in the cap for home loans to Rs. 2 million from Rs. 0.5 million through inclusion in the priority sector, increase in foreign institutional investors limit in rupee denominated corporate bonds from $6 billion to $15 billion exemption of countervailing duty on cement and TMT bars and structural, close monitoring of the government spending to expedite expenditure for all schemes and programmes.
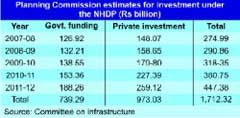
The Planning Commission has estimated that an investment of about $492 billion will be required for the infrastructure sector during the Eleventh Five Year Plan. Whereas private investment seems difficult to come by in the current scenario, public investment can be expected to materialize or even increase. While it is essential that the government plays a vital role in improving the pace of implementation of key projects, construction companies need to upgrade their project management expertise and ensure that there is adequate capacity to undertake and execute projects on time.
Construction Equipment Industry
The ancillary industries including $3.1 billion construction equipment industry has also witnessed a slowdown. Prior to the crisis, the Indian equipment market was growing at a rate of about 35% for almost seven years. However, during October-December 2008 quarter, the growth rate declined by 30%.
To complete critical projects, developers are resorting to selective leasing and renting of equipment. Rental rates have consequently firmed up, benefiting companies involved in the rental business. Further, the price of major input material such as cement and steel has declined significantly, thus somewhat mitigating project costs.
In fact, the fundamentals of the Indian growth story are sound, and the demand for infrastructure and industrial activity continues to be strong. With the government stepping up its support to the infrastructure sectors along with adequate monetary measures aimed at increasing credit flow, the situation is likely to stabilize in the equipment sector, though expectedly with some lag.
Roads & Highways

But with the setting up of an effective public-private partnership (PPP) model by the government to expand the road network, this sector witnessed rapid growth in the past few years and it has become the top contributors to the construction industry. Moreover, the National Highways Development Programme (NHDP) has created the biggest construction opportunity in the road and highways sector. The programme aims at developing 50,000 km of national highways in seven phases by 2015 with an investment of over Rs. 3,000 billion at 2007 prices.
Till January 2009, projects covering 33,000 km under phases I, II, III A and V have been under development out of which about 10,000 km has been four-lane. The Golden Quadrilateral, providing four-lane connectivity to four metros is near completion and the North-South-East West (NSEW) corridor is around 45% complete, whereas Phases III, V and VI are under– implementation. Phases IV and VII are at initial stages of implementation.
The PPP projects for which funds have already been tied up might also face difficulty in drawing down as the risk perception of the sector has risen. Available reports suggest that about 60% of the awarded national highway projects yet to achieve financial closure. In the current scenario, the new highways projects in the private sector may find it tough to achieve financial closure.
Moreover, future prospects for private sector investments in roads would hinge on the effectiveness of the stimulus package in terms of persuading tenders to reassess the risks associated with the sector. National and state level investments in the sector are unlikely to be impacted though the economic slowdown may impact toll collections.
But the road sector, which has already seen a massive shift in the process and mindset, is expected to undergo a further change in the next couple of years. New domestic companies are expected to foray into road development, international players are also expected to enter the Indian road sector and existing players are churning out new strategies to retain their stronghold. With increasing competition, only players with strong organizational structures and project management capabilities are expected to gain ground in the long-term.
Urban Infrastructure
To boost urban infrastructure across the country, the government has initiated multiple measures to lift the infrastructure and construction sectors from the ongoing slowdown and has allocated Rs. 11,842 crore under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM), which is much higher than Rs. 6870 crore sanctioned in the previous budget. The funds aimed at integrated development of urban infrastructure and services in rural areas and urban cities to boost allied sectors including construction material, steel and cement.
In addition, the government has also set aside Rs. 40,900 crore for 2009–10 for its Bharat Nirman initiative. This is a time bound plan for the development of housing, rural roads, power, irrigation, telephony, and drinking water supply. This would in turn boost business opportunities to small and large players alike in the construction and infrastructure as they would offer sizeable scope for contractual work for the local populace.
That apart, the decision of the government to continue with a corpus of Rs. 4,000 crore for rural roads in the Interim Budget has brought cheer to the companies engaged in construction, infrastructure, logistics and transport segments. The move is expected to bring a shift in the supply-chain pattern and improve the delivery of construction materials as due to lack of such facilities in the countryside, the delivery is inadequate both in term of quantity and quality. Today, most of the tier II and III towns are emerging as rural market hubs of production, consumption and distribution.
The government has also launched the Urban Infrastructure Development Scheme for Small and Medium Towns (UIDSSMT) with an outlay of Rs. 64 billion to address infrastructure needs of 5,098 small towns and cities with an outlay of about Rs. 1,064. The JNNURM outlay of over Rs.1 trillion is targeted at augmenting urban infrastructure needs of over 65 mission cities under which the government provides grants ranging from 35% to 90% of the project cost, depending upon the size of the city with state governments and private players contributing the rest.
Moreover, the emphasis on creating infrastructure in villages through Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) has raised hopes for construction and consumer companies hopping that the growing demands from the rural heartland will boost the sagging sectors. Most construction and infrastructure companies from power to roads, airports, ports and urban transport are asking for more in the final budget. Likewise oil & gas, civil aviation, ports, bridges, and semi-urban areas are set to offer lot of opportunities to the construction industryalso to its important constituents like construction equipment, real estate and allied building activities. The measures are bound to lift the commodity linked industries including cement, steel, aluminum, glass, paint, stones, and titles.
The government recent measures focused on encouraging banks to fund PPP projects. This is a positive and progressive move at a time when the financing options of infrastructure players have shrunk in the backdrop of global credit crisis, delaying financial closures. Initially, the banks were demanding a higher equity proportion compared to earlier norms. The refinancing measures will provide better comfort to banks in lending to the infrastructure sector.
Railways & Metro
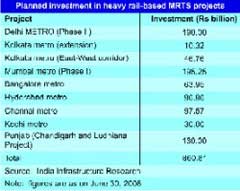
Indian Railways is rapidly consolidating its position and staging a spectacular turnaround largely due to an efficient utilization of resources through increased wagon-loads strictly sticking to its time schedules, and more rational pricing. An investment outlay of Rs. 2,510 billion has been proposed for the Eleventh Plan period, of which around 67% is proposed to be mobilized through internal generation and extra-budgetary resources. Huge opportunities are in the offing in the form of upcoming dedicated freight corridor (DFC) and the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor running along with it, as well as the metro rail projects in about a dozen selected cities of the states.
Infrastructure is being upgraded by way of new railway line projects, gauge conversion, doubling, construction of terminals and logistic parks. As per the eleventh Five Year Plan Working Group Report, the total fund required for capacity enhancement projects during the plan period is Rs. 544 billion, apart from Rs. 70 billion for national railway projects.
In addition, huge construction opportunities are also available for rail-road connectivity and other capacity augmentation projects being undertaken by the Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL). Major opportunities opened up in the modernization projects of 26 railway stations, including those of Delhi and Mumbai to be upgraded on the PPP model. The Indian Railways has decided to attract private investments by allowing areas around stations and above platforms to be commercially developed. This includes separation of operational passenger handling areas from the proposed commercial space as is the case in airports with an estimated investment of about $500 million each.
Vitally, this segment has not been affected by the ongoing global financial crisis because they are funded by the government directly from its own resources. The only noticeable impact can be seen in the segment is the slowdown in freight traffic, which may affect the internal resources of Indian Railways.
That apart, the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) is said to be the biggest venture of Indian Railways to date, envisaging construction of dedicated freight lines on the eastern and western sides of the country, covering 2,729 km through seven states. The two corridors will be interlinked at Khurja and will require a total investment of Rs. 372.18 billion. A special purpose vehicle (SPV), DFC Corporation of India (DFCIL) was set up in 2006 to implement the project with a paid up capital of Rs. 500 million.
Delhi–Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC)
Lauded as the driver for the next level of economic growth of the Indian economy, DMIC has been planned as a global manufacturing and trading hub in India. The dream project involves the development of a 1,500 km industrial belt between Delhi and Mumbai passing through seven states extending upto 150km on either side of the DFC. The investment requirement for the entire DMIC project is Rs. 3,648 billion.
According to sources, 24 industrial development hubs have been identified in the form of industrial regions for development across the corridor. The Phase 1 of the project between Delhi and Vadodara will be carried out during 2008-12 and Phase II will be extended till 2013-18. The project will have enormous potential for development in terms of industrial growth and employment. In a five year period, it is envisaged to double the employment potential upto 14.87% compounding annual growth rate to be triple of the industrial output of about 24.57% and quadruple exports from the region is expected to be 31.95% with a total employment potential of about 0.8 million masses.
Metro Rail Projects
Real Estate
Falling inflation, interest rates and above all the recent fiscal stimulus announced by the government, will give indirect push to construction and housing activities across the country. Steel players will benefit from government measures such as bringing HR coils under the restricted category and levy of import duty on flat products. The reduction of excise duty in cases where the output is sold directly to the consumer, withdrawal of export duty on iron ore fines and export duty reduction on iron ore lumps and pellets will encourage iron ore exports, besides encouraging developers to focus on affordable housing.
Recently, the centre has given a major incentive to the states to engage private developers by agreeing in doling out 25% of the total cost of external services such as drainage, roads, sewage and a water supply as grant to state governments. Consequently, the meltdown may soon make housing for the masses a reality. The Centre has been awaiting a reply from state governments on its Rs. 5,000 crore package to create on million affordable houses across the country. In the recent past, developers have also announced plans to foray into the affordable housing segment. The leading players in the real estate business have also unveiled plans to build houses in the 20 lakh category. In fact, the meltdown may soon make housing for the masses a reality.
Power Sector

Meeting the projected target, the Union Government has decided to add about 78,000 MW of power generation capacity during the Eleventh Plan period. The generation capacity additional needs are being complemented by commensurate investments in transmission and distribution networks.
In the recent past, the sector has witnessed increased investment interest from private players especially in the generation segment and in the past half decade the trend has registered consistent growth. The demand supply gap of about 16% as peak shortage and 10% as average shortage indicates a huge opportunity for developers and their financiers including power equipment suppliers. The generation segment has grown at an annual rate of 5.6% during the period and transmission and distribution segment have also grown at an annual rate of 3% and 1.5% respectively. In the past couple of years, the power generation pace has grown from 124.287 MW in 2005–06 to 143.061 in 2007–08 and the Electricity Act 2003 is said to be the main driver behind the marked growth.
Conclusion
Now the construction activities have started picking up. Recently, the Government has issued contracts worth Rs 1,861 crore relating to projects in mining, railway, infrastructure, commercial buildings, and some of the construction companies are also coasting along with a steady flow of contracts. About 90% of these contracts are from the Government agencies and this is going to be the mainstay of business in construction sector for some time to come till such orders start flowing from the private sector. It is indeed to the credit of some of the construction companies that despite odds, these companies have shown exemplary perseverance in tackling recession to carry out construction work, others would also ride well through the present dull phaseas the situation improves. It is expected that sooner rather than later, the sleepy construction project sites would pulsate with construction work once again and one would see trucks loads of men, materials and machinery moving to and frowith men and women working on a war footing to translate country’s development vision into a concrete reality. Shedding its initial pessimism, the construction equipment sector is also getting into optimistic mode and is busy in giving final touches to their expansion plans to add new manufacturing facilities sensing a demand pull in the next 6-8 months. All in all, the construction industry was no doubt downbut not out.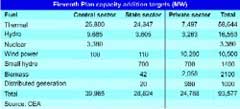
NBM&CW April 2009


















